Abstract
White nationalism – a belief system that champions white racial superiority and promotes the vision of a racially homogeneous society – poses a profound threat to contemporary democracies. This paper delves into the ideology’s historical origins, core principles, and modern expressions. It outlines the serious consequences of white nationalism, including its erosion of social harmony, democratic structures, and fundamental human rights. Drawing on case studies and evidence, the paper illustrates how this ideology fosters systemic inequality, incites violence, and dismantles pluralism. The conclusion emphasises the urgency of addressing white nationalism through strategies like education, policy-making, and community-based initiatives.
Introduction
White nationalism is a far-right ideology advocating for societies exclusively composed of white individuals. Its underlying beliefs rest on notions of racial dominance and the preservation of an idealised white culture. Though its roots lie in colonialism and eugenics, the modern resurgence of white nationalism has been fuelled by a combination of factors, including globalisation, economic anxieties, and the influence of social media. This paper explores the risks white nationalism poses to society and offers analysis into its implications.
Historical Context
Colonialism and Eugenics
White nationalism is founded on the racial hierarchies established during colonialism and shaped by eugenicist theories, which rationalised the oppression of non-white populations. These historical ideologies laid the groundwork for contemporary attitudes of racial superiority. Colonial powers often justified their expansionist policies through the belief in the civilising mission, positioning non-white cultures as inferior and in need of domination.
Twentieth-Century Movements
In the 20th century, white nationalist ideology manifested in systems such as South African apartheid and America’s Jim Crow laws. It also underpinned fascist regimes like Nazi Germany, which pursued racial “purity” through policies of extermination and exclusion. The atrocities committed during these periods exemplify the extreme consequences of unchecked white nationalist ideologies.
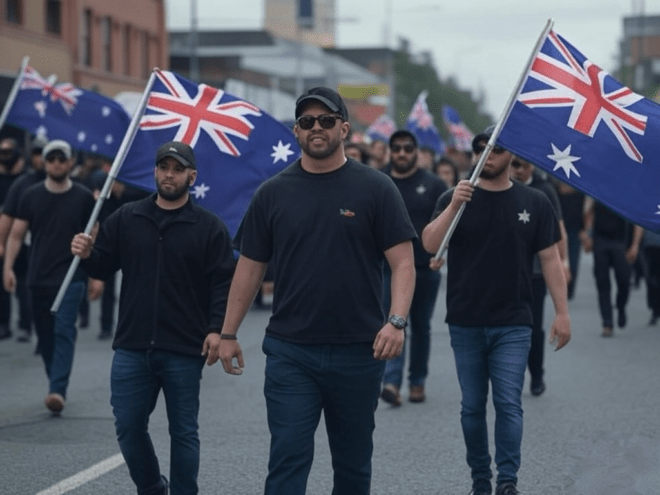
Contemporary Revival
In recent years, white nationalism has experienced a resurgence, often disguised as a defence of heritage or opposition to immigration. The populist wave and the amplification of white nationalist beliefs within public arenas have brought these ideas back into the spotlight, fuelling the growth of extremist groups. The internet has played a crucial role in this revival, facilitating the spread of propaganda and connecting like-minded individuals across borders.
Ideological Foundations
The Myth of Racial Superiority
White nationalists espouse the false notion of white racial superiority, often bolstered by pseudoscientific arguments. This ideology blatantly contradicts the values of equality and human dignity that are central to functional democracies. The belief in a hierarchy of races undermines social cohesion and fosters environments conducive to discrimination and violence.
Preservation of White Culture
Adherents argue that globalisation and multiculturalism threaten white culture, framing their views as efforts to protect tradition. This perspective vilifies diversity and positions non-white cultures as inherently lesser. Such narratives often gain traction during periods of social upheaval, where individuals seek to reclaim a perceived lost identity.
Opposition to Immigration
White nationalists frequently decry immigration from non-white regions, claiming it erodes cultural identity and national integrity. These anti-immigration stances are rooted in fears of demographic shifts and the perceived loss of white dominance. Politically, this rhetoric has been utilised to galvanise support for restrictive immigration policies, further entrenching divisions within society.
Modern-Day Expressions
Political Influence
White nationalist narratives have permeated the political mainstream across nations such as the United States, Europe, and Australia. Movements like the alt-right and xenophobic rhetoric from political leaders demonstrate the alarming normalisation of these beliefs. Political parties advocating for white nationalist policies have gained representation, indicating a significant shift in the political landscape.
Social Media Radicalisation
Digital platforms serve as a powerful vehicle for spreading white nationalist propaganda, enabling rapid dissemination of extremist ideologies. Algorithm-driven content amplification fosters echo chambers and accelerates radicalisation. The role of social media in promoting hate speech and facilitating violent mobilisation cannot be overstated.
Acts of Violence
White nationalism has been directly associated with numerous violent incidents, including the 2019 Christchurch mosque shootings and the 2017 Unite the Right rally in Charlottesville. These events underscore the real and devastating impact of this dangerous worldview. The connection between ideology and violence highlights the urgent need for intervention.
The Dangers of White Nationalism – Erosion of Democracy
Undermining Diversity
White nationalism threatens democratic principles of equality and inclusion by promoting exclusionary ideologies. This weakens the representation of marginalised groups in political processes. A healthy democracy relies on the active participation of diverse voices; when these voices are silenced, democracy itself is undermined.
Deepening Divisions
The ideology intensifies social and political polarisation, hindering consensus-building and effective governance. Such divisions can destabilise democracies and erode shared societal norms. The increasing partisanship associated with white nationalist rhetoric has led to legislative gridlock and societal unrest.
Fostering Division and Hate
By inciting racial and ethnic tensions, white nationalism creates an atmosphere of hostility, discrimination, and violence. This weakens trust and cooperation within communities. Social cohesion is critical for societal progress, and the promotion of hate fractures the very fabric of community life.
Marginalisation of Minority Groups
The rise of white nationalist sentiment leads to increased exclusion and systemic disadvantages for non-white populations, impacting access to resources such as education and employment. This marginalisation perpetuates cycles of poverty and disenfranchisement, further entrenching societal divides.
Violations of Human Rights
Perpetrating Violence
Many white nationalist groups are linked to acts of terrorism and harassment targeting racial, ethnic, and religious minorities. These acts not only harm individuals but instill widespread fear. The psychological impact of such violence can reverberate throughout entire communities, leading to long-term trauma.
Institutional Discrimination
The ideology reinforces structural racism, perpetuating inequities in education, housing, and job opportunities. Such systemic bias undermines the foundation of an equal and just society. Addressing these inequalities requires concerted efforts at both policy and community levels.
Case Studies
In the United States
The Capitol insurrection on January 6, 2021, highlighted the influence of white nationalist ideologies within American politics. Many participants were driven by beliefs in white supremacy and unfounded claims of electoral fraud, exemplifying the risks this ideology poses to democratic processes. This event serves as a stark reminder of the potential for violence and chaos when extremist beliefs infiltrate the political sphere.
Across Europe
In Europe, white nationalist-linked parties like France’s National Rally and Germany’s Alternative for Germany (AfD) have gained substantial electoral traction. Their platforms often combine anti-immigration policies with nationalist rhetoric, fostering deeper societal divisions. The electoral success of these parties reflects a growing acceptance of white nationalist ideologies within mainstream politics.
In New Zealand
The 2019 Christchurch mosque attacks exposed the global spread of white nationalist extremism. The assailant’s manifesto, rooted in white nationalist ideology, demonstrated how these beliefs can transcend borders and inspire violence worldwide. The international ramifications of such ideologies necessitate a collective response from governments and civil society.
Combating White Nationalism
Education
Encouraging critical thinking and raising awareness about historical and cultural diversity can help dismantle the myths perpetuated by white nationalist ideologies. Educational initiatives focused on inclusivity play a key role in countering hateful narratives. Comprehensive education systems that promote tolerance and understanding are vital for fostering a more equitable society.
Legislative Measures
Governments must take decisive action by implementing laws against hate speech, monitoring extremist activities, and addressing structural inequalities. Strong policies create safeguards for vulnerable communities and uphold democratic principles. Legislative frameworks should be designed to promote inclusivity and protect the rights of all citizens.
Community-Driven Solutions
Fostering dialogue among diverse groups and building inclusive communities are essential steps in reducing the allure of white nationalism. Grassroots efforts promote understanding, cooperation, and solidarity. Community initiatives that celebrate diversity and address grievances can mitigate the appeal of extremist ideologies.
Conclusion
The dangers of white nationalism to democracy, social unity, and human rights cannot be overstated. Its rise in the modern era calls for determined efforts to counter its influence. By addressing its root causes and striving for more equitable societies, humanity can reject divisive ideologies and pave the way for a fairer future. The fight against white nationalism is not only a political battle but a moral imperative that requires collective action from individuals, communities, and governments worldwide.